AI-DRIVEN ISCHEMIC STROKE DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
Project background:
The rising number of radiological exams highlights the pressing need for faster and more accurate diagnoses.
Biggest challenges: Complex data description and computer vision training due to the wide variation in data – different features may be present for the same diagnosis.
Solution:
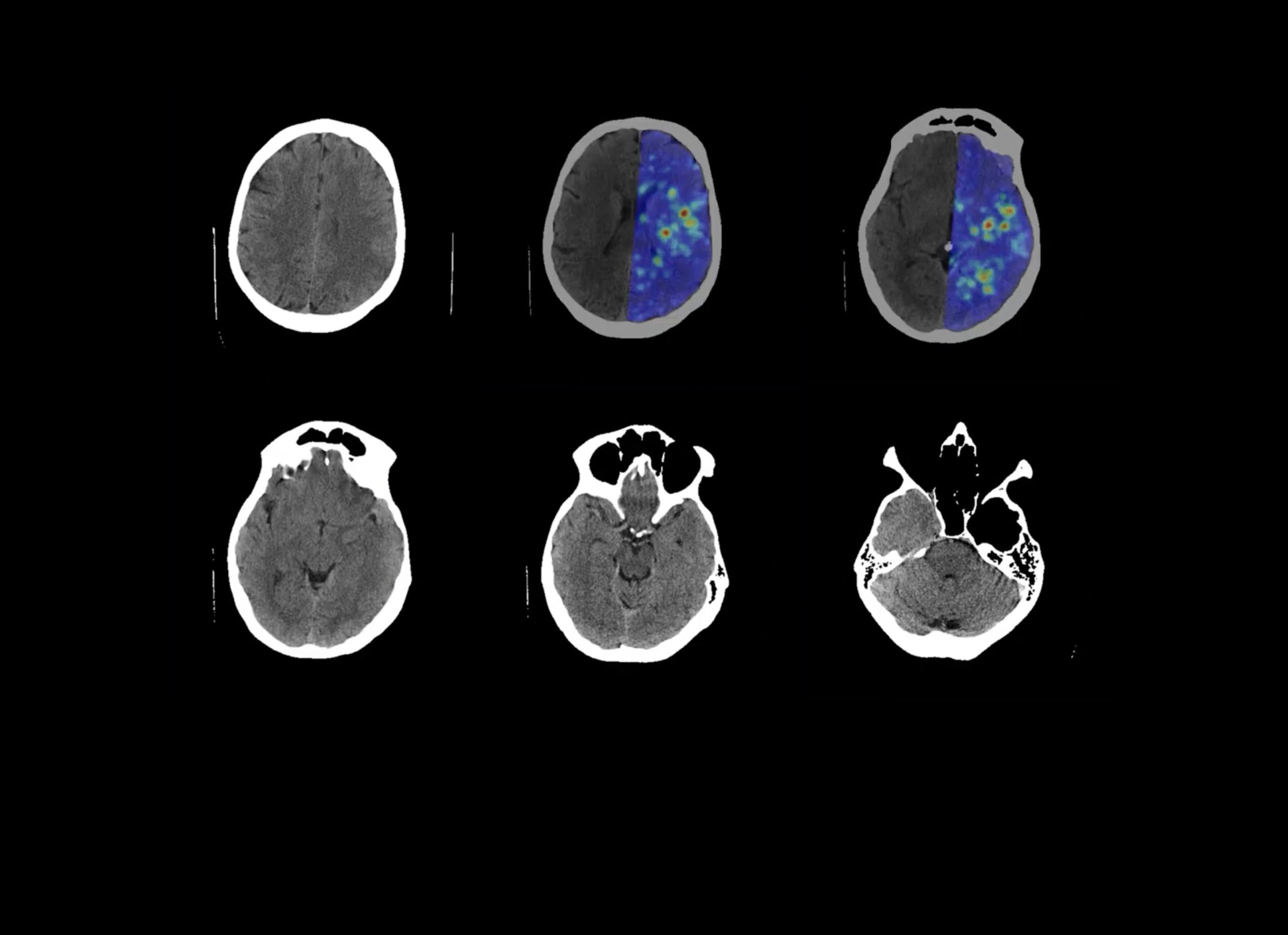
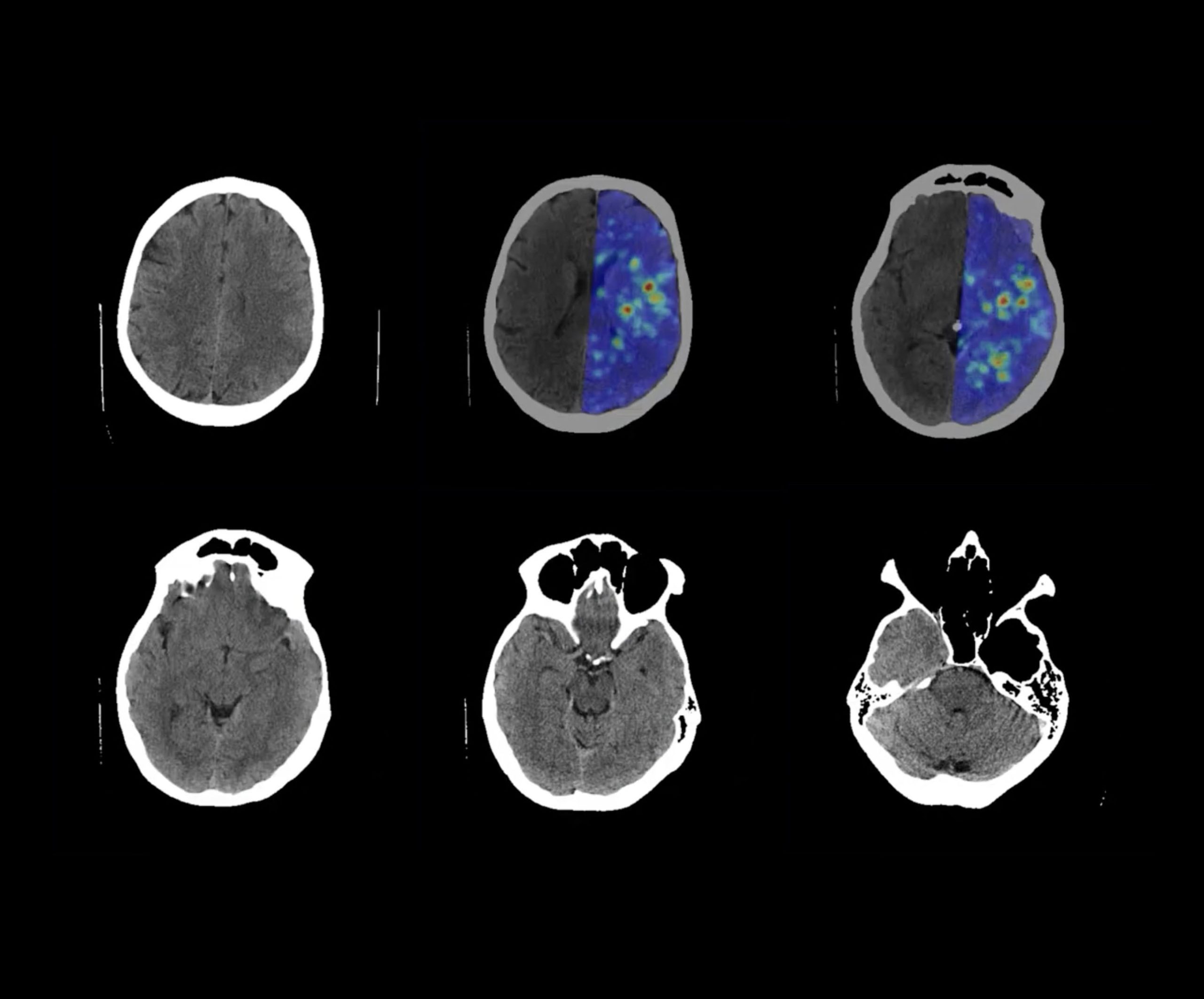
The solution is a prototype tool that uses computer vision algorithms and a set of neural network models to perform a fully automated analysis of a brain CT scan. System can identify possible brain pathologies and determine if a patient is experiencing an acute stroke. It is able to accurately identify, classify and localise acute stroke, other types of abnormalities and norm.
The solution consists of several components that perform following processes: automated reception of data from the hospital CT scanner, anonymization of the data, and data transmission to an AI service for processing. The AI processing service performs automated processing of complete examination, analysing each layer of the examination, describing results and sending them to the hospital’s internal application, which is used to view and analyse patient data.
AI component of the solution consists of computer vision algorithms and neural network models that are specifically designed and trained for the solution. This was the result of an extensive study that led to the development of a complex solution.
Solution also includes a common data description methodology and a common data description tool for maximum accuracy and quality to ensure the highest possible data purity.
The solution has been integrated into the PSCUH (Pauls Stradiņš Clinical University Hospital)system since March 2024 and it is being tested and used as a tool to support daily work in diagnostics.
Key benefits:
- The Acute stroke diagnostic system is already able to work with 93% accuracy, which is far more accurate than experienced diagnostician;
- Time for diagnosis is shortened, which can be crucial in cases of ischemic stroke;
- Decreased workload for medical personell in the reception department.